School Bus E-Learning App
What is an E-Learning App?
An online learning app is a digital platform for education and skill development. They offer courses, tutorials, lectures, and quizzes to learn at your own pace. They often cover a wide range of subjects from English to Math or practical skills like programming and language learning. E-Learning apps are an accessible way for people to acquire knowledge or improve their skills with an online connection.
What is School Bus?
An online learning app that acts like a virtual school for users of grades 5th-12th. It offers a wide range of interactive courses covering essential school subjects like Math, English, Science, and History. Just like hopping on a real school bus, users can embark on a journey of knowledge exploration right from their devices.
Problem Definition
There is a significant gap in access to quality education, with many individuals unable to access or afford high-quality educational resources. The lack of access discourages individuals and their ability to acquire basic knowledge and skills needed for personal growth and career advancement.
The Goal
The goal for School Bus is to provide accessible, affordable, and high-quality educational resources to individuals worldwide, regardless of their geographical location, financial status, or other barriers. School Bus aims to promote inclusivity by offering personalized learning experiences.

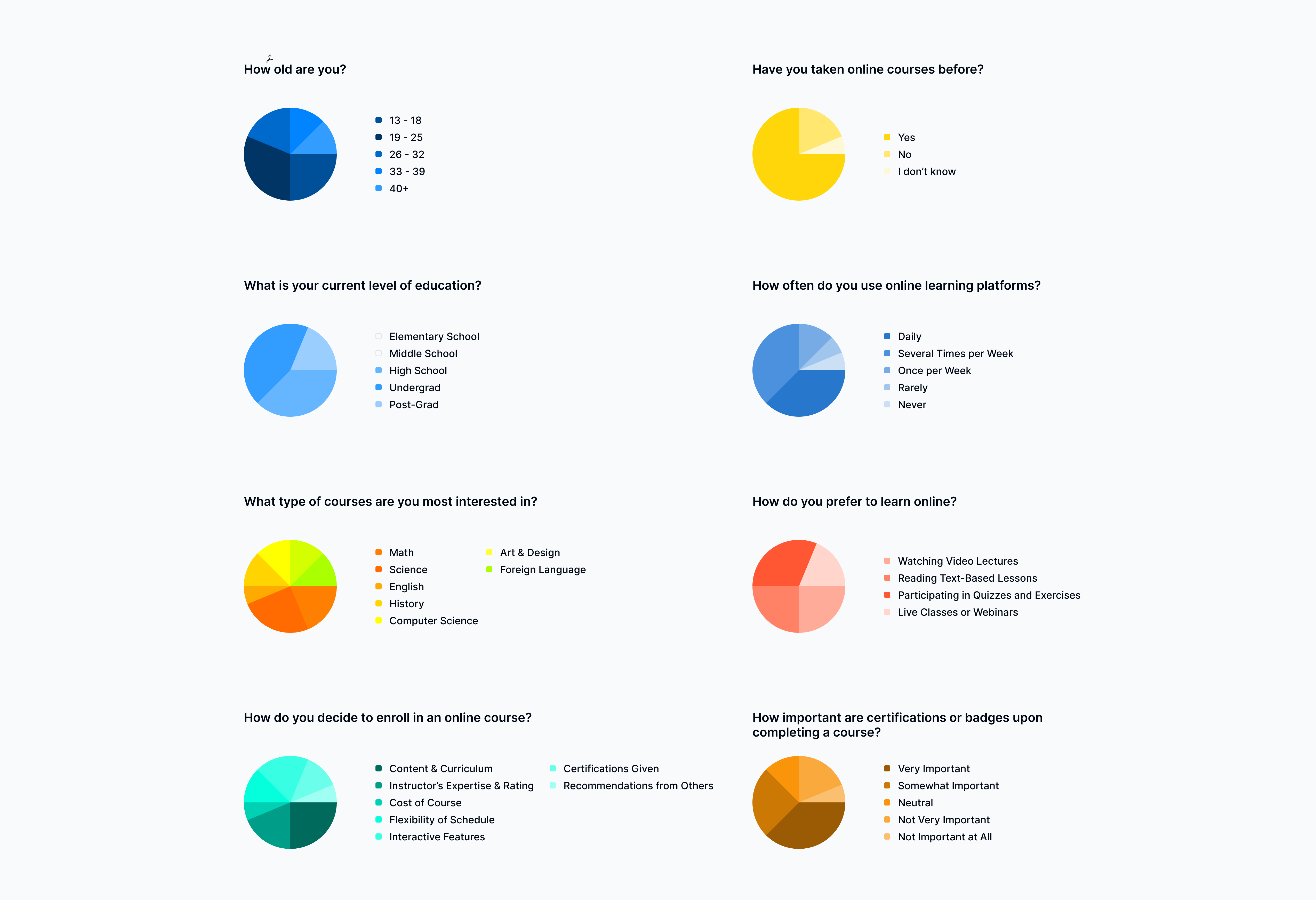
Survey Questions & Responses
Feedback Summary
I conducted a survey asking users about their expertise on E-learning platforms. Based on the 16 responses from the survey about online learning platforms, users are mostly between the ages of 19-25 followed by ages 26-32 in the Undergrad and Post-grad stages of their lives. A majority of the respondents have taken online courses before, while few have not. The respondents often use online learning platforms either Daily or Several Times per Week with very few only using them Once per Week or Rarely and Never.
Respondents showed more interest in the Math and Science course subjects with little interest in English. They prefer to learn online by Participating in Quizzes and Exercises compared to Live Classes or Webinars.
Content and Curriculum was the highest rated response for how respondents decide to enroll in an online course. The Instructor’s Expertise and Rating and Interactive Features followed after with Recommendations from Others being the least chosen response.
Respondents find it to be Very Important to receive Certifications or Badges upon course completion with very few finding it Not Important at All.
It appears there is a strong demand for online education, but with interactive learning methods and a focus on the quality of content and instructor’s knowledge. Additionally, offering certifications or badges upon a course’s completion drives the user’s engagement and will.
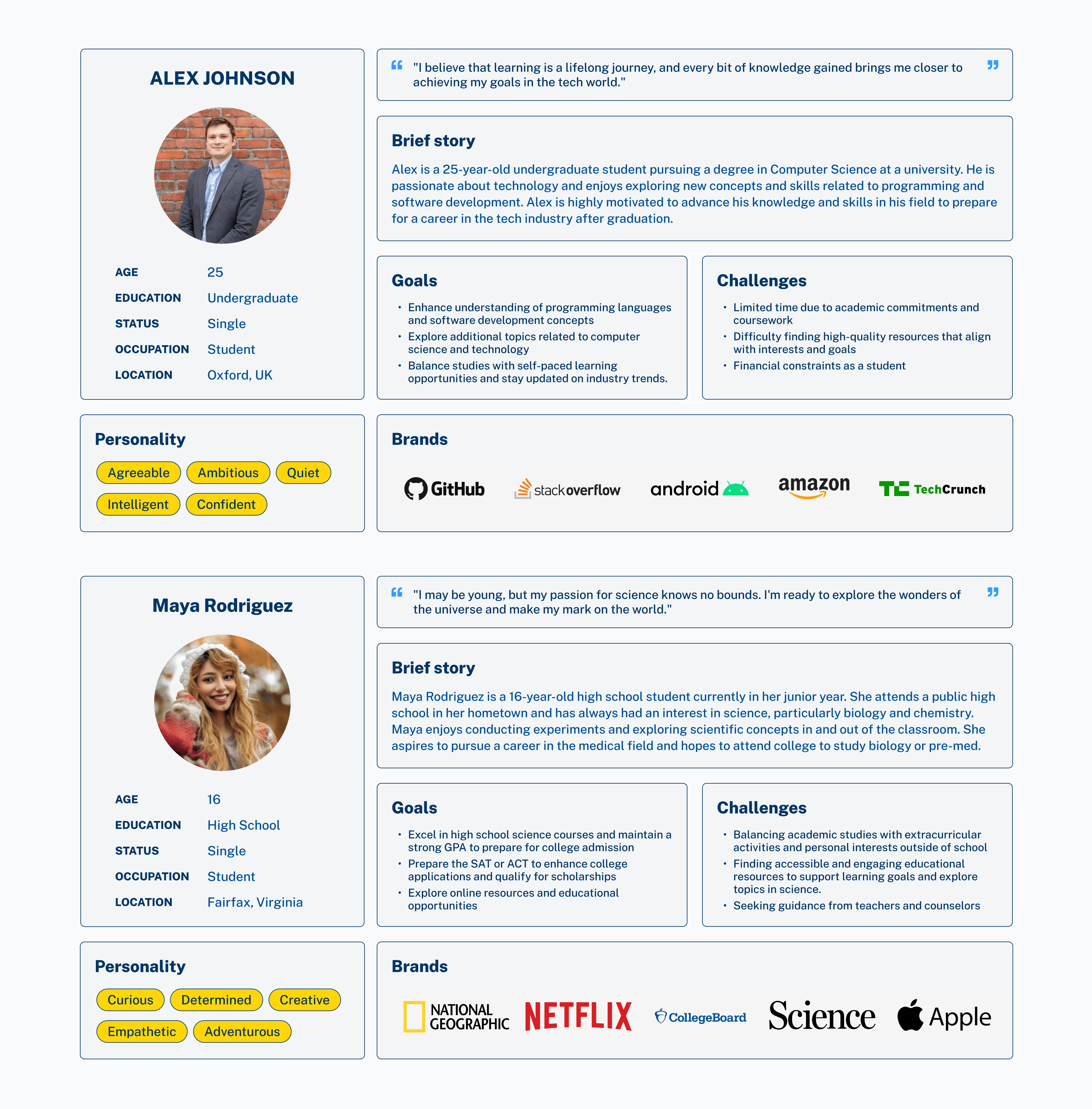
User Personas
Designing the User Personas
Each user persona consists of a male and female user. The male user persona is a twenty-five year old undergrad student pursuing a degree in computer science. The user wants to develop their skills as a programmer as well as exploring additional topics not learnt in school. The problems the user faces are limited time constraints, difficulty finding high-quality resources, and financial constraints.
The female user persona is a high school student with a keen interest in science. The user hopes to excel in the science background in high school in order to attend a good university to pursue a career in the medical or science field. The user’s goals are to explore additional resources and educational opportunities to advance in her studies. The challenges the user faces are balancing her studies with the extracurricular activities and finding accessible and engaging educational resources.
Empathy Maps
Designing the Empathy Maps
Each of the two empathy maps support the users’ thoughts, feelings, and actions. The male empathy map follows what he says, thinks, feels, and does. The sections relate to his passion for programming and development. For example, he feels frustrated when encountering coding challenges or he goes out of his way to participate in doing workshops.
The female empathy map follows what she says, feels, thinks, and does all similarly to the male empathy map. All of her thoughts and feelings are relating to her passions in the field of science. For example, she says she is fascinated by genetics and biology. She also feels curious about exploring new scientific concepts.

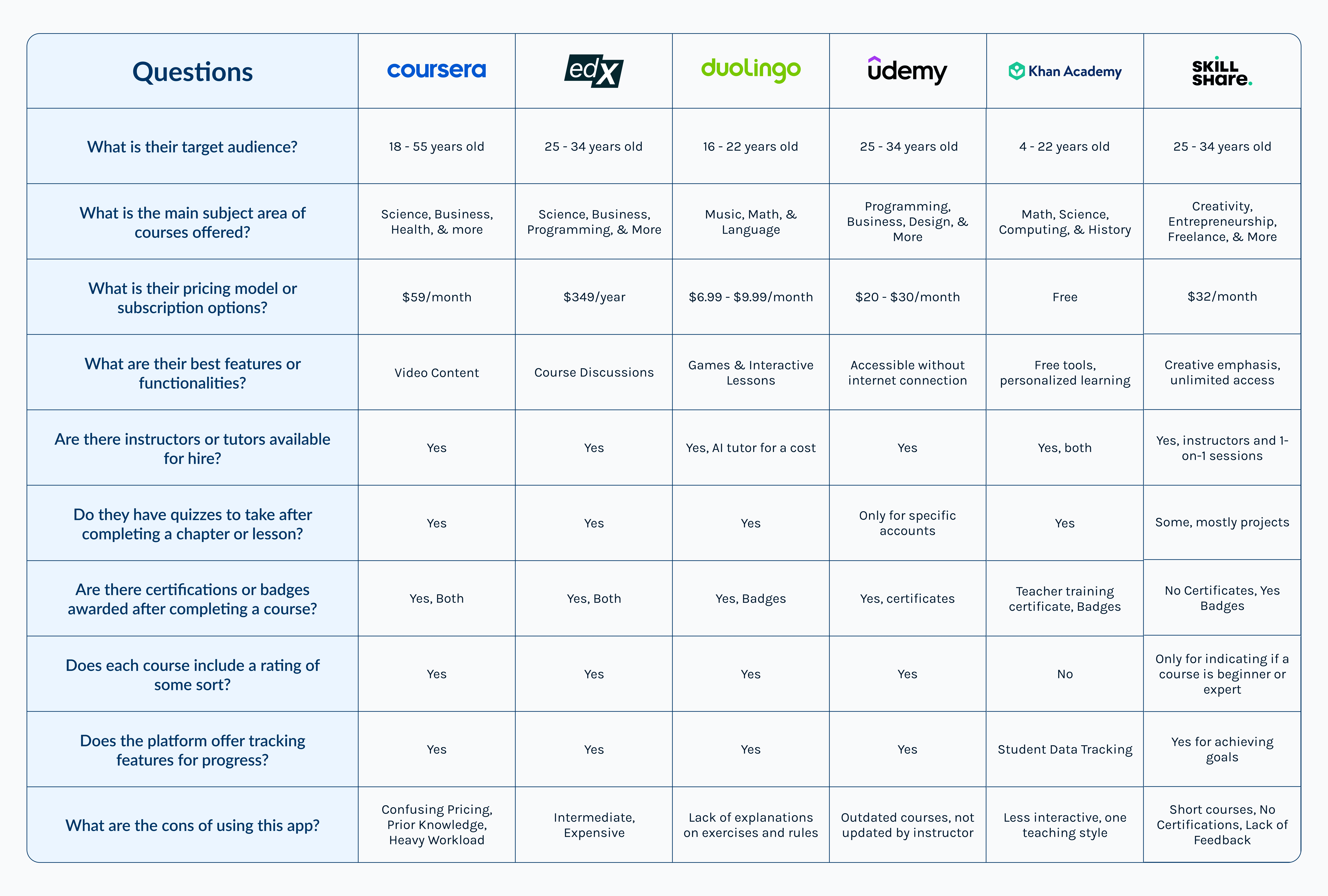
Competitor Research
Researching the Competitors
The competitor research chart asks questions relating to the six different E-learning applications: Coursera, Duolingo, Udemy, Khan Academy, and Skill Share. During my research, I found each platform has most subjects of courses or they more relate to coding and programming. Each age group is roughly around the mid-twenties mark and most of the platforms but one have a subscription fee.
Khan Academy appeared to be the best platform due its widened age range. They have a variety of subjects from math to history and are a free platform. The only downside to the platform is that it is less interactive than the other E-learning apps with one specific teaching style.
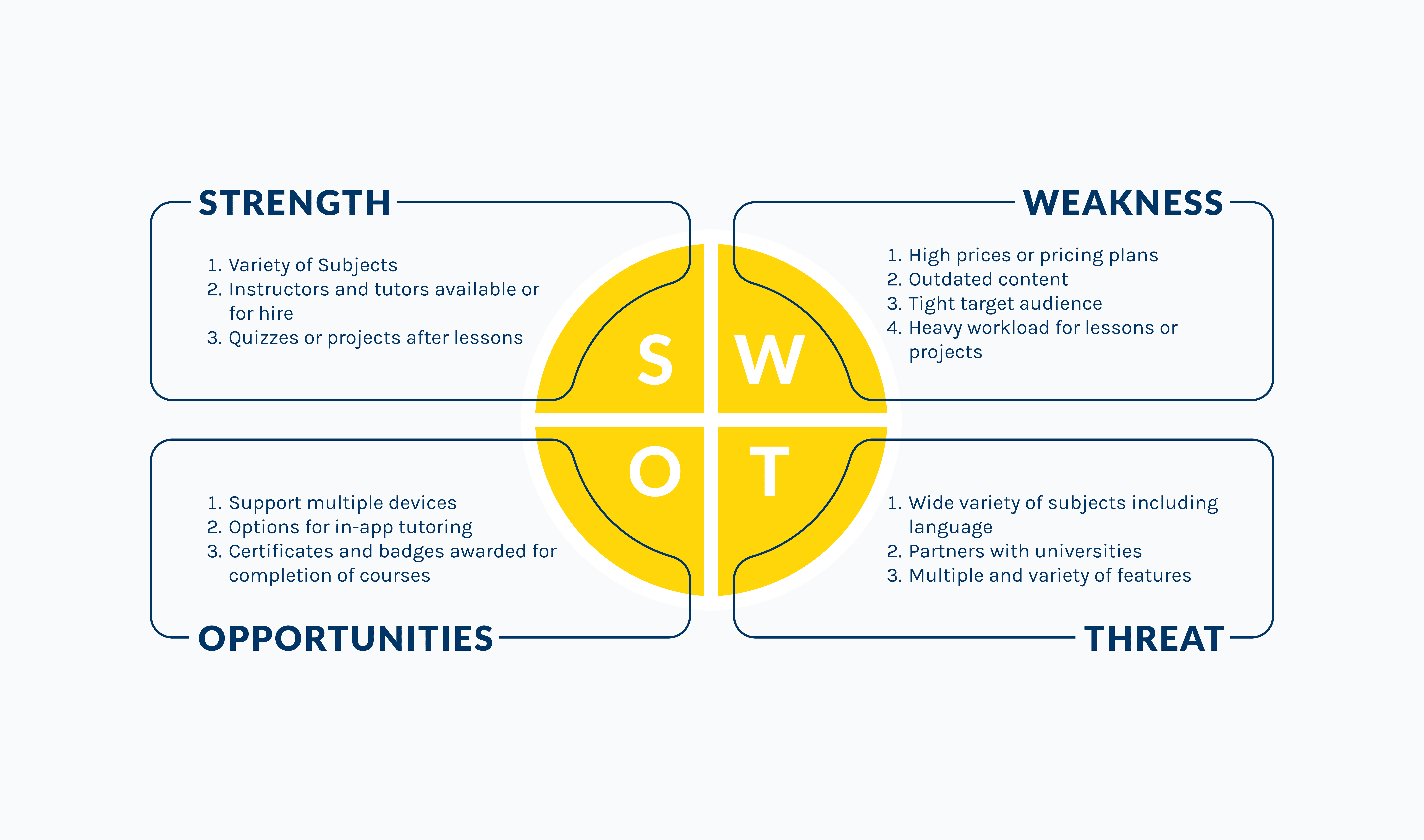
SWOT Analysis
Analyzing the SWOT
A SWOT Analysis examines the competitors Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. A strength of the SWOT Analysis chart data is that each platform includes a variety of subjects from Math, Science, History, and English. If a platform is based on a single subject, there are multiple types of videos for that one subject. An opportunity of the data includes support for multiple devices and options for in-app learning and tutoring.
A weakness of the data showed that the platforms either had too high of prices or pricing plans whereas only one platform was entirely free. Another weakness was that there is outdated content or instructors don’t update their plans when needed. A threat of the data showed that there are a variety of subjects and many of the platforms partner with universities for certificates and degrees.
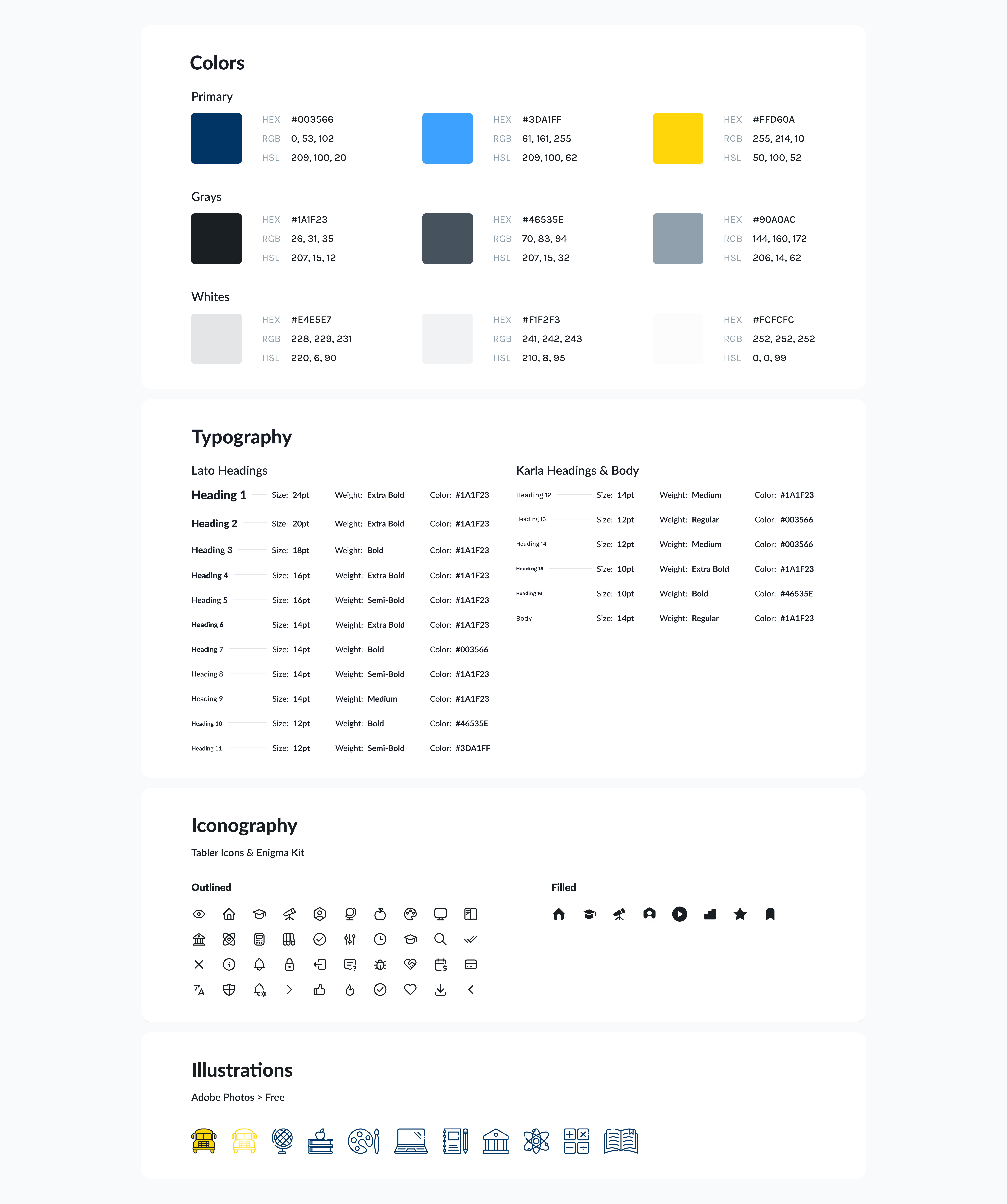
Style Guide
Designing the Style Guide
The Style Guide consists of Colors, Typography, Iconography, and Illustrations. The color palette in the app uses blue and yellow as the primary colors with an array of grays with a hint of blue as secondary colors. For fonts, I used Late for headings and Karla for secondary headings and body text. The icons come from Tabler Icons and Enigma Kit, both available in the Figma community. The illustrations are from Adobe Photo’s Free section and edited within Adobe Illustrator.
Low-Fidelity Wireframes
Lo-Fi Process
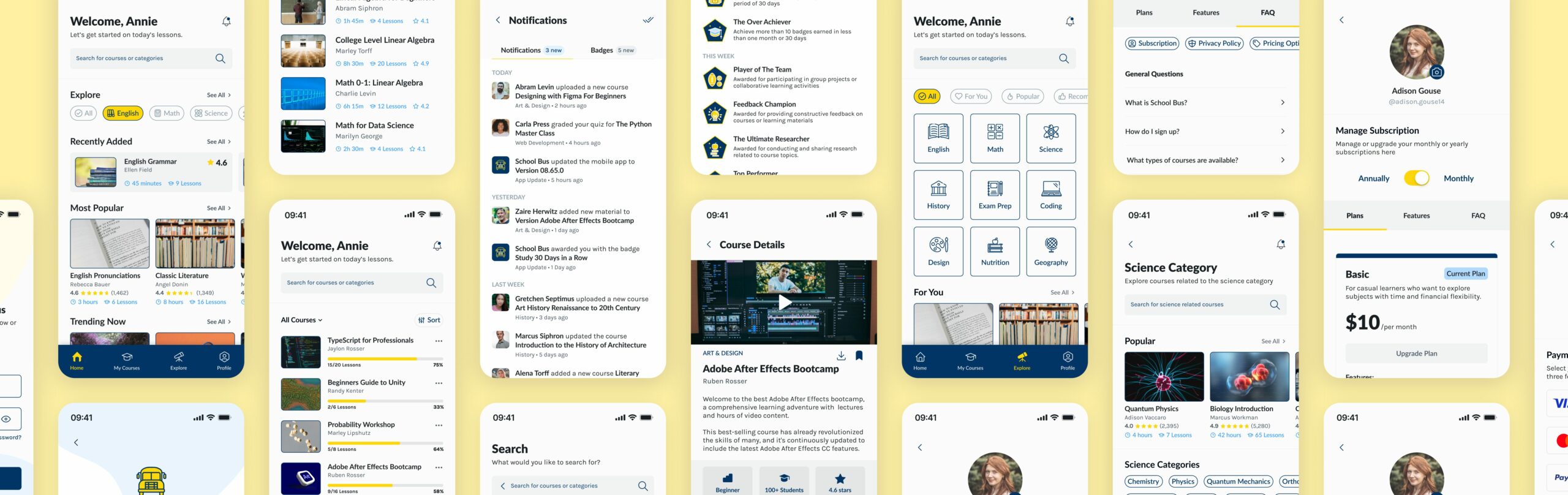
After conducting my research and developing my style guide, I created the lo-fi wireframes within Figma. I began the process with a Splash Screen where users can select to create an account or log into their account. From there, users can either sign up or log in and be directed to the home page. The layout of the home page includes several categories for recent courses uploaded to the app. From the home page, users can explore the app’s other screens: My Courses, Explore, and Profile.
The My Courses screen holds all of the user’s current courses they are studying. A progress bar shows the number of videos needed to play in order to complete the course.
The Explore screen allows users to explore all subjects and categories on the app. Users can find new courses they have not heard of before or they can find similar courses to ones they’ve just completed. The layout is simple and easy to use so users can easily find what they are looking for.
The Profile screen includes all the basic information for a user’s profile. Users can choose to edit their profile if they wish or they can change their subscription plan. In the Change Subscription screens, users can slide between Plans, Features, and FAQ. Lastly, users can also update their payment method by choosing a method of payment or entering in a new credit card.

The Final Design
Design Explanation
Once completing the low-fidelity wireframes for the School Bus app, I began to design the high-fidelity wireframes of the app, making slight changes along the way. The structure of the app takes the user through the app’s entirety. Beginning on the Splash Screen, users can choose to either Login to Sign Up. The background of the app uses a deep navy blue as the app’s primary color with yellow being used as the fill or outline of the buttons. If users would rather explore the app, they can select Continue as a Guest instead of signing into the app.
The Login screen of the app features two abstract elements in a low opacity blue and yellow. Users are requested to sign in with their email and password. Or users can sign in with their Google, Facebook, or Apple accounts. The Sign Up page features similar information and elements but users are asked for their full name and password twice.
Once a user has logged into the app, they are directed to the Home Screen. This screen features a wide search bar for courses and categories. The Search function opens a new screen where users can view popular searches as quick links or they can type into the search bar themselves. When a user has types into the search bar, they will see results pop up in the form of cards which feature the cover image, title/author, rating of the course, and the number of lessons. The Filter button opens another screen where users can filter out specific information such as the Level of courses, Ratings, Lesson Duration, and Features. Back at the home page, users can select a specific category to view its most popular or trending courses. From the Home Screen, the user is directed to the My Courses screen.
My Courses allows users to see all of their current courses. Each course card features the cover image to the far left with the course title and author to the right. Each card contains a progress bar which includes the number of lessons completed and remaining with a percentage of the course completion. The Sort option allows users to be able to sort the courses by recently opened, percentage, and lessons. The All Courses button allows users to be able to sort their courses by category. Users may share or download the course offline if they please. To the top right of each screen is a bell icon.
The Notification screen includes a menu for Notifications or Badges. The Notifications screen includes cards featuring a cover image to the left with the alert description to the right. The Badges screen includes a similar format but with Badges as the cover image and the title and description of that badge to the right. The Badge illustrations are from Adobe Photos, redesigned in Illustrator. From the My Courses screen, the user taps on a course and is directed to Course Details.
The Course Details screen features a cover video as the top center item of the screen. Below, users can read more into the course’s description and view the Level, number of students, and rating. The lesson plan is laid out below the course description showcasing each lesson to be watched. Users can view all of the categories contained within this course. Below those categories, users can read more into the instructor and their background as well as read into the course ratings. The bottom of the screen features similar courses the user can browse as well. The user will have to click the chevron icon at the top left of the screen in order to be taken back to the My Courses screen to be able to move forward onto other screens.
The Explore screen features two sets of categories. The first category asks the user what popularity of content they would like to search for: All, For You, Popular, and Recommended. The second category asks the user what subjects they would like to search for: English, Math, Science, History, Exam Prep, Coding, Design, Nutrition, and Geography. Finally, users can browse that content below once selecting their respective categories.
Once a user selects a subject category, they will be carried over to that specific screen. For example, the Science Category screen contains a tab for the popular courses. Each card features a top cover image followed by the card’s information. Below those cards, users can browse categories specifically within that category such as: Chemistry, Physics, and Quantum Mechanics. The categories are more specific to the category. Below those categories, users can browse through more Science categories.
Once the user has browsed through the Explore section of the app, they will be directed to their Profile screen. The main profile screen has options to change the user’s account or give support. One of the main functions of the Profile screen is to edit your profile. The Edit Profile screen allows users to change their full name, gender, birthdate, email, and phone number.
Another screen users can edit in the Profile screen is the Change Subscription screen. This screen allows users to manage their subscription from annually or monthly and select or update their payment plan. Users can also browse through each plan’s features and read through frequently asked questions.
If a user changes their subscription plan or signs up for the app’s subscription service, they can add a payment method by either selecting one of their previously added credit cards or adding a new credit card. The Add Payment Method screen includes an option to add your credit card number, the name on card, expiration date, CVC, and a promo code if necessary.

The Video
About the Prototype
The video prototype uses smooth and simple animations to get from one screen to another. While most interactions are instant, some use move in animations to smoothly move in menus. Some screens also use move in animations when going from one screen to another. The video prototype was edited in Premiere Pro and recorded with Quick Time.